H502
Contents
Overview
H502 is an ultra-thin one-piece copper heatsink specially designed for Raspberry Pi 5 Model B. CNC-processed copper heatsink with precise cutouts, designed to seamlessly fit the Raspberry Pi 5B motherboard.
Through-hole screw holes allow expansion boards installed on top of the H502 heatsink or on the bottom of the H502 heatsink. H502 also supports 30x30mm cooling fan installation for better heat dissipation.
Geekworm Cooler Series:
| Picture | Model | Compatible With | Material | Thickness(mm) | Support Fan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C519 | Raspberry Pi Computer Module 5 (CM5) | Aluminum Alloy | 15mm | √ support fan installation | |
| Pi 5 official Active Cooler | Raspberry Pi 5 | Aluminum Alloy | 10mm | √ with 4-pin 3007 blower fan | |
| H505 | Raspberry Pi 5 | Aluminum Alloy | 11.6mm / Net Weight: 39g | √ with 4-pin 3007 blower fan | |
| H509 | Raspberry Pi 5 | Aluminum Alloy | 15mm | × don't support fan installation | |
| H510 | Raspberry Pi 5 | Brass | 10mm / Net Weight: 55g | √ with 4-pin 3007 blower fan | |
| Argon THRML 30-AC | Raspberry Pi 5 | Aluminum Alloy | 9.6mm | √ with 4-pin 3007 blower fan | |
| H501 | Raspberry Pi 5 | Aluminum Alloy | 9.5mm | √ with 4-pin 3007 blower fan | |
| H502 | Raspberry Pi 5 | Brass | 4mm | × support 30x30 fan installation | |
| P165-B | Raspberry Pi 4 | Aluminum Alloy | 11mm | × support 30x30 fan installation | |
| P165-A | Raspberry Pi 4 | Aluminum Alloy |
7mm/8mm (Version updated; 2 versions available, 8mm (new), compatibility unaffected) |
× support 25x25 fan installation | |
| H402 | Raspberry Pi 4 | Brass | 4mm | × don't support fan installation | |
| C235 | Raspberry Pi Computer Module 4 (CM4) | Aluminum Alloy | 12mm | × support 30x30 fan installation | |
| C296 | Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W | Aluminum Alloy | 10mm | × don't support fan installation |
Features
- Model: H502
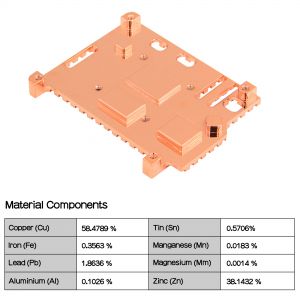
- Material: copper
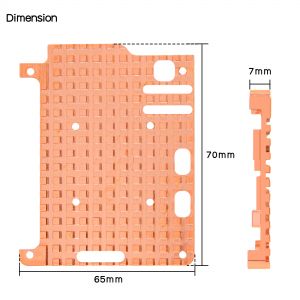
- heartsink Thickness: 4mm / 0.16inch
- Heatsink Net Weight: 63g / 0.14lb
- Through-hole screw holes allow expansion boards installed on the top of heatsink or on the bottom of raspberry pi
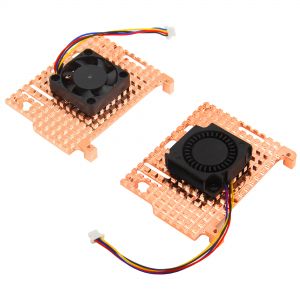
- Supports 30x30mm fan installation for active cooling
- Comes with thermal pads for both CPU,RAM,USB chip and network module of Raspberry Pi 5
- Includes an acrylic plate for installing under the Raspberry Pi 5 to provide protection



Enable comment auto-refresher
Anonymous user #2
Permalink |
Lisa
Anonymous user #2
Permalink |
Lisa
Anonymous user #2
Permalink |
Lisa
Anonymous user #2
Permalink |
Anonymous user #1
Permalink |