Difference between revisions of "X729-Software"
| (42 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{GD Template Impl}} | {{GD Template Impl}} | ||
| − | The following test is base on | + | <big>Although this installation tutorial is still available, but we strongly recommend that you use [[X729-script]] new tutorial, and we no longer maintain this page.</big> |
| + | |||
| + | ==Setup script== | ||
| + | The following test is base on | ||
| + | * [https://downloads.raspberrypi.org/raspios_arm64/images/raspios_arm64-2023-05-03/2023-05-03-raspios-bullseye-arm64.img.xz 2023-05-03-raspios-bullseye-arm64.img.xz] | ||
| + | * [https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/ 2022-09-22-raspios-bullseye-armhf.img.xz] | ||
| + | * [https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/ 2022-09-22-raspios-buster-armhf.img.xz] | ||
| + | |||
| + | PS: To buster version, the default user name is 'pi, but bullseye version, you need to manually create a new user. In our example script, the new user name we created is 'pi'. If you create your own user name, you need to modify the corresponding user name directory in the script. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For Example: You may need to change '/home/pi/' => '/home/XX/', 'XX' is user name you created. | ||
Python version is 3; | Python version is 3; | ||
| − | '''1. Enable I2C funcion on Raspbian | + | ==='''1.Enable I2C funcion on Raspbian'''=== |
| − | |||
| − | '''2. Check & review I2C | + | Please reter to [[How to enable I2C]] |
| + | |||
| + | ==='''2. Check & review I2C address'''=== | ||
2.1 Login via teminal window, then update & upgrade & install necessary software (python and i2c tool library) | 2.1 Login via teminal window, then update & upgrade & install necessary software (python and i2c tool library) | ||
sudo apt-get update | sudo apt-get update | ||
| − | sudo apt-get upgrade | + | sudo apt-get -y upgrade |
| − | sudo apt-get -y install i2c-tools python3-smbus | + | sudo apt-get -y install i2c-tools python3-smbus python3-rpi.gpio |
| − | |||
sudo apt-get -y install python3-pip python3-pil | sudo apt-get -y install python3-pip python3-pil | ||
| + | |||
| + | #sudo apt-get -y install pigpio python-pigpio python3-pigpio | ||
2.1 Once you have logged into your Raspberry Pi from the command line, run the command to see all the connected devices | 2.1 Once you have logged into your Raspberry Pi from the command line, run the command to see all the connected devices | ||
| Line 28: | Line 40: | ||
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 68 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | 60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 68 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | ||
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | 70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- | ||
| + | </PRE> | ||
| + | Explaination: | ||
| + | <PRE> | ||
#36 - the address of the battery fuel gauging chip | #36 - the address of the battery fuel gauging chip | ||
| − | #3c - OLED | + | #3c - address of oled display,This value only exists when the oled is inserted,check if the OLED is inserted in the correct direction if you don't found the above i2c port |
#40 - TI INA219 12-bit current/voltage/power monitor | #40 - TI INA219 12-bit current/voltage/power monitor | ||
#68 - the address of the RTC chip | #68 - the address of the RTC chip | ||
| Line 36: | Line 51: | ||
PS: Please check if the OLED is inserted in the correct direction if you don't found the above i2c port | PS: Please check if the OLED is inserted in the correct direction if you don't found the above i2c port | ||
| − | '''3. Setting up the power management script''' | + | ==='''3. Setting up the power management script'''=== |
3.1 Download x729 setup scripts: | 3.1 Download x729 setup scripts: | ||
| Line 43: | Line 58: | ||
3.2. Install script&reboot: | 3.2. Install script&reboot: | ||
| + | cd x729 | ||
| + | chmod +x *.sh | ||
sudo bash pwr.sh | sudo bash pwr.sh | ||
| − | |||
| + | #Setting up the command to turn off X729 from software | ||
printf "%s\n" "alias x729off='sudo x729softsd.sh'" >> ~/.bashrc | printf "%s\n" "alias x729off='sudo x729softsd.sh'" >> ~/.bashrc | ||
| − | #Reboot the Raspberry Pi | + | |
| − | sudo reboot | + | #Reboot the Raspberry Pi or long press on-board button switch to turn off |
| + | sudo reboot now | ||
3.3 Powering off the Raspberry Pi from software | 3.3 Powering off the Raspberry Pi from software | ||
x729off | x729off | ||
| + | * x729off is safe shutdown command | ||
| + | * press on-board blue button 1-2 seconds to reboot | ||
| + | * press on-board blue button 3 seconds to safe shutdown, | ||
| + | * press on-board blue button 7-8 seconds to force shutdown. | ||
| − | '''4. Setting up the PWM cooling fan''' | + | ==='''4. Setting up the PWM cooling fan'''=== |
cd ~ | cd ~ | ||
cd x729 | cd x729 | ||
| Line 77: | Line 99: | ||
python3 read_fan_speed.py | python3 read_fan_speed.py | ||
| − | '''5. Test PLD/PLSD/buzzer function''' | + | ==='''5. Test PLD/PLSD/buzzer function'''=== |
| + | |||
5.1 Test AC Power loss or power adapter failure detection (PLD) | 5.1 Test AC Power loss or power adapter failure detection (PLD) | ||
| Line 90: | Line 113: | ||
pi@raspberrypi:~/x729 $ sudo python3 plsd.py | pi@raspberrypi:~/x729 $ sudo python3 plsd.py | ||
Safe shutdown will be implemented in 5 seconds. | Safe shutdown will be implemented in 5 seconds. | ||
| + | |||
5.3 Test the buzzer alarm when AC power loss or power adapter failure | 5.3 Test the buzzer alarm when AC power loss or power adapter failure | ||
| Line 97: | Line 121: | ||
Once power adapter is removed then the buzzer will generate a beep sound continuously. | Once power adapter is removed then the buzzer will generate a beep sound continuously. | ||
| − | '''6. Set and Read the RTC time''' | + | |
| + | ==='''6. Set and Read the RTC time'''=== | ||
6.1 Run the following command on your Raspberry PI to begin editing the /boot/config.txt file. | 6.1 Run the following command on your Raspberry PI to begin editing the /boot/config.txt file. | ||
| Line 109: | Line 134: | ||
Save and exit. In nano, you do that by hitting CTRL + X, answering Y and hitting Enter when prompted. | Save and exit. In nano, you do that by hitting CTRL + X, answering Y and hitting Enter when prompted. | ||
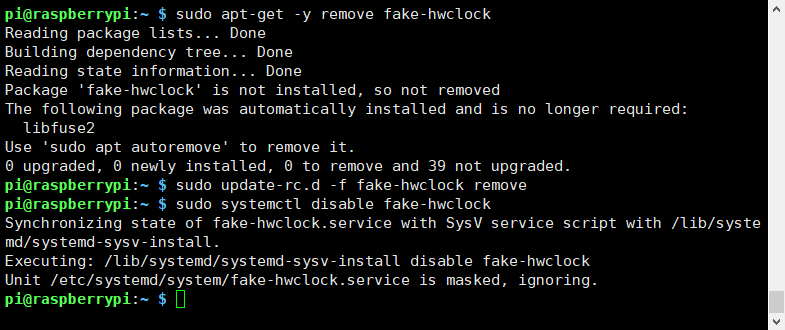
| − | Run the commands to disable the "fake hwclock" which interferes with the 'real' hwclock | + | 6.2 Run the commands to disable the "fake hwclock" which interferes with the 'real' hwclock |
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo apt-get -y remove fake-hwclock | pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo apt-get -y remove fake-hwclock | ||
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo update-rc.d -f fake-hwclock remove | pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo update-rc.d -f fake-hwclock remove | ||
| Line 115: | Line 140: | ||
[[File:X729-6.png|none]] | [[File:X729-6.png|none]] | ||
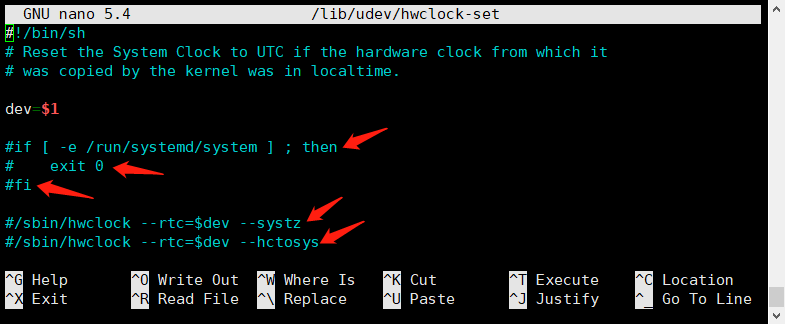
| − | + | 6.3 Run the command and comment out these five lines: | |
| − | Run the command and comment out these five lines: | + | sudo nano /lib/udev/hwclock-set |
[[File:X729-7.png|none]] | [[File:X729-7.png|none]] | ||
| − | 6. | + | 6.4 Reboot the Raspberry Pi |
| − | + | pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo reboot | |
| − | + | 6.5 Run the command to verify the time is correct. Plug in Ethernet or WiFi to let the Pi sync the right time from the Internet | |
| − | + | pi@raspberrypi ~ $ date | |
| − | + | 6.6 Run the command to write the time | |
| − | + | pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo hwclock -w | |
| − | + | 6.7 Run the command to read the time | |
| − | + | pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo hwclock -r | |
| − | + | Once the time is set, make sure the batteries are inserted so that the time is saved. You only have to set the time once. That's it! Next time you boot the time will automatically be synced from the [[X729]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===7. How to enable automatic shutdown when low voltage=== | |
| − | sudo | + | 7.1 Run the command to read battery voltage and percentage |
| + | pi@raspberrypi:~/x729 $ sudo python3 bat.py | ||
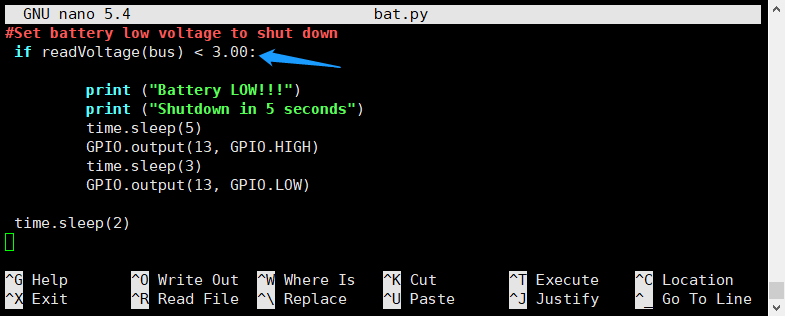
| + | 7.2 Change the battery low voltage to implement safe shutdown. default is less than 3.00Vdc. | ||
| + | pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo nano bat.py | ||
| + | [[File:X729-3.png|none]] | ||
| + | Note: the voltage range must be 2.5~4.1vdc. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | 7.3 Optional - if you want to run Python Script automatically on Bootup then run the command | |
| + | pi@raspberrypi:~/x729 $ sudo crontab -e | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
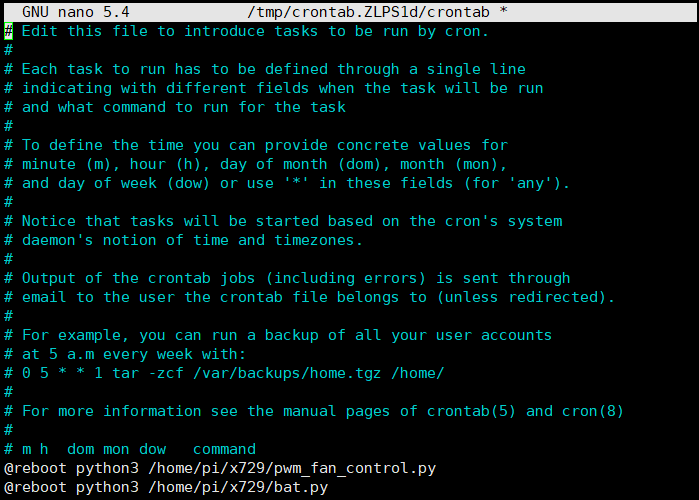
| − | + | 7.4 Add a line at the end of the file that reads like this: | |
| − | + | @reboot python3 /home/pi/x729/bat.py | |
| − | + | [[File:X729-4.png|none]] | |
| − | + | Save and exit. In nano, you do that by hitting CTRL + X, answering Y and hitting Enter when prompted. | |
| − | == | + | ===8. How to enable OLED display=== |
| − | + | Refer to [[How to enable OLED display]] | |
| − | + | ==Uninstall cript== | |
| − | + | uninsatll x729 shell script, run the following command: | |
| + | sudo ./uninstall_x729.sh | ||
| − | + | ==Other resource== | |
| + | X729-Chip-Specifications: | ||
* [[File:MAX17040-MAX17041.pdf]] | * [[File:MAX17040-MAX17041.pdf]] | ||
| Line 183: | Line 194: | ||
*[https://www.instructables.com/Raspberry-Pi-Tutorial-How-to-Use-a-Buzzer/ Raspberry Pi Tutorial: How to Use a Buzzer] | *[https://www.instructables.com/Raspberry-Pi-Tutorial-How-to-Use-a-Buzzer/ Raspberry Pi Tutorial: How to Use a Buzzer] | ||
| − | Return to [[ | + | |
| + | Return to [[X729]] or [[X729-hardware]] | ||
<!--Add review function! --> | <!--Add review function! --> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:11, 23 July 2023
Although this installation tutorial is still available, but we strongly recommend that you use X729-script new tutorial, and we no longer maintain this page.
Contents
- 1 Setup script
- 1.1 1.Enable I2C funcion on Raspbian
- 1.2 2. Check & review I2C address
- 1.3 3. Setting up the power management script
- 1.4 4. Setting up the PWM cooling fan
- 1.5 5. Test PLD/PLSD/buzzer function
- 1.6 6. Set and Read the RTC time
- 1.7 7. How to enable automatic shutdown when low voltage
- 1.8 8. How to enable OLED display
- 2 Uninstall cript
- 3 Other resource
Setup script
The following test is base on
- 2023-05-03-raspios-bullseye-arm64.img.xz
- 2022-09-22-raspios-bullseye-armhf.img.xz
- 2022-09-22-raspios-buster-armhf.img.xz
PS: To buster version, the default user name is 'pi, but bullseye version, you need to manually create a new user. In our example script, the new user name we created is 'pi'. If you create your own user name, you need to modify the corresponding user name directory in the script.
For Example: You may need to change '/home/pi/' => '/home/XX/', 'XX' is user name you created.
Python version is 3;
1.Enable I2C funcion on Raspbian
Please reter to How to enable I2C
2. Check & review I2C address
2.1 Login via teminal window, then update & upgrade & install necessary software (python and i2c tool library)
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get -y upgrade sudo apt-get -y install i2c-tools python3-smbus python3-rpi.gpio sudo apt-get -y install python3-pip python3-pil #sudo apt-get -y install pigpio python-pigpio python3-pigpio
2.1 Once you have logged into your Raspberry Pi from the command line, run the command to see all the connected devices
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo i2cdetect -y 1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- 36 -- -- -- -- -- 3c -- -- --
40: 40 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 68 -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
Explaination:
#36 - the address of the battery fuel gauging chip #3c - address of oled display,This value only exists when the oled is inserted,check if the OLED is inserted in the correct direction if you don't found the above i2c port #40 - TI INA219 12-bit current/voltage/power monitor #68 - the address of the RTC chip
PS: Please check if the OLED is inserted in the correct direction if you don't found the above i2c port
3. Setting up the power management script
3.1 Download x729 setup scripts:
cd ~ git clone https://github.com/geekworm-com/x729
3.2. Install script&reboot:
cd x729 chmod +x *.sh sudo bash pwr.sh #Setting up the command to turn off X729 from software printf "%s\n" "alias x729off='sudo x729softsd.sh'" >> ~/.bashrc #Reboot the Raspberry Pi or long press on-board button switch to turn off sudo reboot now
3.3 Powering off the Raspberry Pi from software
x729off
- x729off is safe shutdown command
- press on-board blue button 1-2 seconds to reboot
- press on-board blue button 3 seconds to safe shutdown,
- press on-board blue button 7-8 seconds to force shutdown.
4. Setting up the PWM cooling fan
cd ~ cd x729 python3 pwm_fan_control.py
4.1 Run the script at Raspberry Pi boot
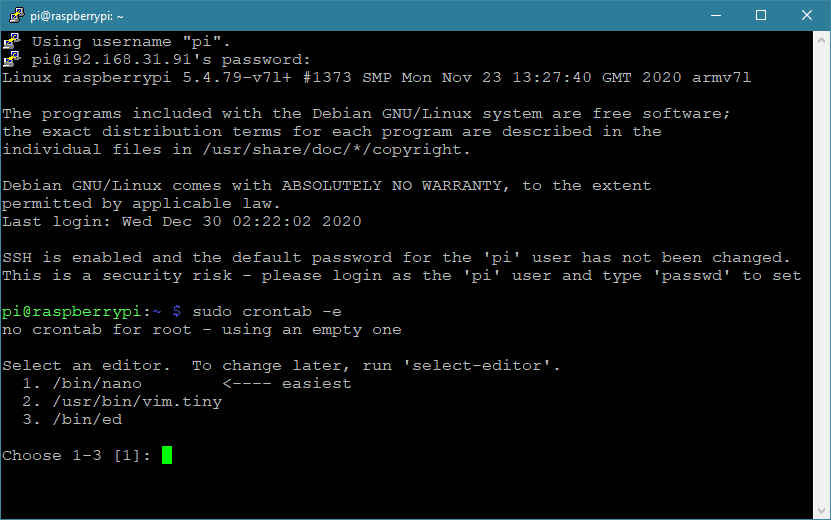
sudo crontab -e
Choose "1" then press Enter
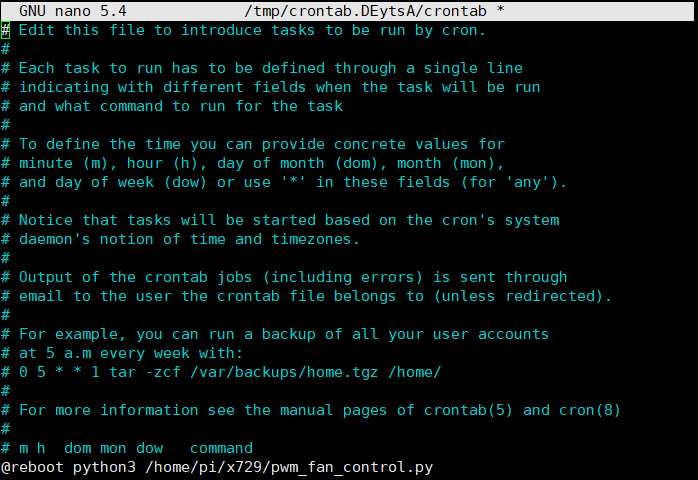
4.2 Add a line at the end of the file that reads like this:
@reboot python3 /home/pi/x729/pwm_fan_control.py
4.3 Save and exit. In nano, you do that by hitting CTRL + X, answering Y and hitting Enter when prompted.
4.4 Run below script and you will get RPM value every second:
cd ~ cd x729 python3 read_fan_speed.py
5. Test PLD/PLSD/buzzer function
5.1 Test AC Power loss or power adapter failure detection (PLD)
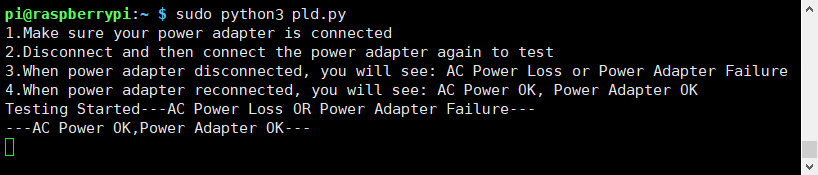
Run the script test the PLD function
sudo python3 pld.py
5.2 Test Auto shutdown when AC power loss or power adapter failure
Run the script and then remove your power adapter
pi@raspberrypi:~/x729 $ sudo python3 plsd.py
Safe shutdown will be implemented in 5 seconds.
5.3 Test the buzzer alarm when AC power loss or power adapter failure
Run the script and unplug your power adapter from the UPS.
pi@raspberrypi:~/x729 $ sudo python3 buzzer.py
Once power adapter is removed then the buzzer will generate a beep sound continuously.
6. Set and Read the RTC time
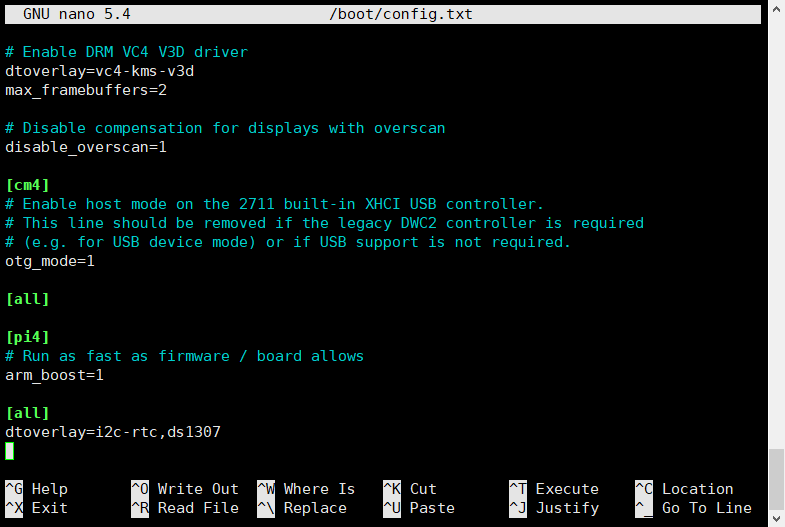
6.1 Run the following command on your Raspberry PI to begin editing the /boot/config.txt file.
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
add one of the following lines to the bottom of the file,
dtoverlay=i2c-rtc,ds1307
Save and exit. In nano, you do that by hitting CTRL + X, answering Y and hitting Enter when prompted.
6.2 Run the commands to disable the "fake hwclock" which interferes with the 'real' hwclock
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo apt-get -y remove fake-hwclock pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo update-rc.d -f fake-hwclock remove pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo systemctl disable fake-hwclock
6.3 Run the command and comment out these five lines:
sudo nano /lib/udev/hwclock-set
6.4 Reboot the Raspberry Pi
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo reboot
6.5 Run the command to verify the time is correct. Plug in Ethernet or WiFi to let the Pi sync the right time from the Internet
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ date
6.6 Run the command to write the time
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo hwclock -w
6.7 Run the command to read the time
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo hwclock -r
Once the time is set, make sure the batteries are inserted so that the time is saved. You only have to set the time once. That's it! Next time you boot the time will automatically be synced from the X729.
7. How to enable automatic shutdown when low voltage
7.1 Run the command to read battery voltage and percentage
pi@raspberrypi:~/x729 $ sudo python3 bat.py
7.2 Change the battery low voltage to implement safe shutdown. default is less than 3.00Vdc.
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo nano bat.py
Note: the voltage range must be 2.5~4.1vdc.
7.3 Optional - if you want to run Python Script automatically on Bootup then run the command
pi@raspberrypi:~/x729 $ sudo crontab -e
7.4 Add a line at the end of the file that reads like this:
@reboot python3 /home/pi/x729/bat.py
Save and exit. In nano, you do that by hitting CTRL + X, answering Y and hitting Enter when prompted.
8. How to enable OLED display
Refer to How to enable OLED display
Uninstall cript
uninsatll x729 shell script, run the following command:
sudo ./uninstall_x729.sh
Other resource
X729-Chip-Specifications:
References:
Return to X729 or X729-hardware
Enable comment auto-refresher
Anonymous user #2
Permalink |
Anonymous user #3
Anonymous user #1
Permalink |
Walker