Difference between revisions of "CSI Audio Video capturing using GStreamer"
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 16:24, 27 June 2023
This article describes how the X630 can be combined with the X630-A2 to capture stereo sound Audio and Video using GStreamer
Capturing stereo audio with the X630-A2 from the HDMI source is supported.
If you need to run RASPISTILL or RASPIVID again after the GStreamer is installed. You will need to reinstall a fresh Raspberry Pi OS and follow this guide
1. After the device is booted, update your Raspberry Pi by running the following commands in a terminal window:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade -y
2. Install necessary dependency and remaining plugins for GStreamer
sudo apt-get install libx264-dev libjpeg-dev sudo apt-get install libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-bad1.0-dev gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-tools
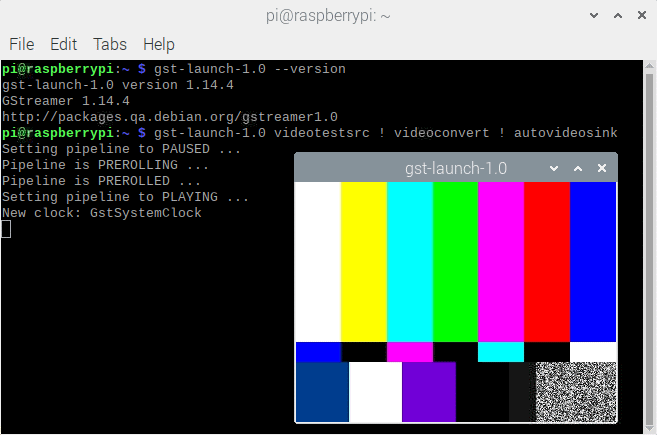
3. With all GStreamer modules installed let's test the installation with (not via SSH)
gst-launch-1.0 --version gst-launch-1.0 videotestsrc ! videoconvert ! autovideosink
4. Edit /boot/config.txt and enter the following
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Then add the following comments:
dtoverlay=tc358743 dtoverlay=tc358743-audio dtoverlay=cma,cma-128
Save and exit with ctrl + x, followed by y when prompted to save, and then enter.
5. Reboot the Raspberry Pi
sudo reboot
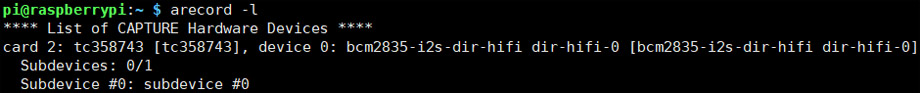
6. Once rebooted and check that the audio drivers / card is available to ALSA.
arecord -l
If the X630 module and drivers have been installed correctly you should see something similar to:
Note: card 2 means that the card number for the TC358743XBG is "2" and it might be different.
7. Create an EDID file so it can be loaded into the chip to allow it to tell the HDMI source what resolutions are supported.
sudo nano edid.txt
then enter the following:
00ffffffffffff005262888800888888 1c150103800000780aEE91A3544C9926 0F505400000001010101010101010101 010101010101011d007251d01e206e28 5500c48e2100001e8c0ad08a20e02d10 103e9600138e2100001e000000fc0054 6f73686962612d4832430a20000000FD 003b3d0f2e0f1e0a202020202020014f 020321434e041303021211012021a23c 3d3e1f2309070766030c00300080E300 7F8c0ad08a20e02d10103e9600c48e21 0000188c0ad08a20e02d10103e960013 8e210000188c0aa01451f01600267c43 00138e21000098000000000000000000 00000000000000000000000000000000 00000000000000000000000000000028
Save and exit with ctrl + x, followed by y when prompted to save, and then enter.
8. Push this to the device using
v4l2-ctl --set-edid=file=edid.txt --fix-edid-checksums
9. To print the currently detected timings
v4l2-ctl --query-dv-timings
10. To select the currently detected timings
v4l2-ctl --set-dv-bt-timings query
11. Capture the incoming audio (no video)
arecord -D hw:x,0 -V stereo -r 48000 -f S16_LE -c 2 audio.wav
Note: hw:x - You must replace "x" with correct audio card number.
Press ctrl + c to finish a recording, the file will be saved to /home/pi
12. Capture the incoming video and audio
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src io-mode=0 ! video/x-raw, format=UYVY, framerate=25/1 ! v4l2h264enc output-io-mode=4 ! video/x-h264,profile=high ! h264parse ! queue ! matroskamux name=mux ! filesink location=video.mkv alsasrc device=hw:2 ! audio/x-raw,rate=48000,channels=2 ! audioconvert ! avenc_aac bitrate=48000 ! aacparse ! queue ! mux.
Note: alsasrc device=hw:2 - "2" means the audio card number, You must change to correct audio card number.
Press ctrl + c to finish a recording, the file will be saved to /home/pi
Enable comment auto-refresher